
Lipid Problems
What is Lipid Problems?
Lipid problems, also known as lipid disorders or dyslipidemia, refer to abnormalities in the levels of lipids (fats) in the blood. Lipids are essential molecules that include cholesterol and triglycerides, which are important for cell structure, energy storage, and hormone production. However, when lipid levels become too high or too low, it can lead to health complications, particularly related to heart disease and stroke.
What are the types of Lipid Problems?
Cholesterol:
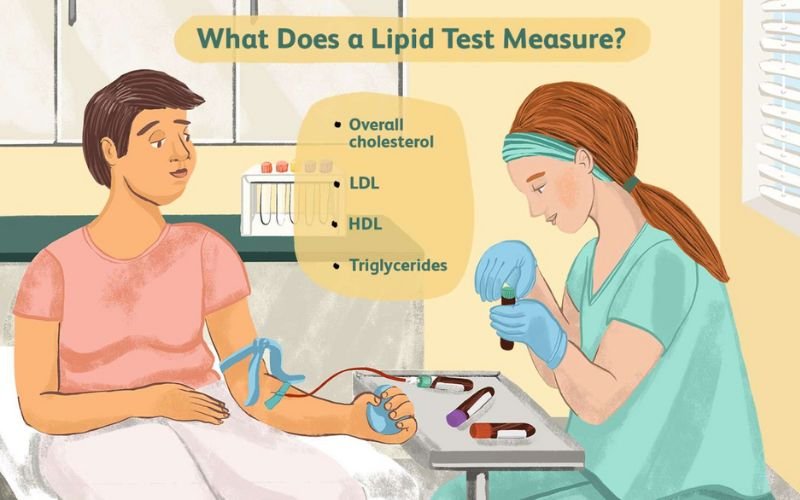
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Known as “bad” cholesterol. High levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Known as “good” cholesterol. HDL helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transports it to the liver for elimination.
- Total Cholesterol: A measure of all cholesterol in your blood, including LDL and HDL.
Triglycerides: Another type of fat in the blood. High levels of triglycerides, especially in combination with high LDL or low HDL, can increase the risk of heart disease.
Common Lipid Problems:
Hypercholesterolemia (High Cholesterol): This condition involves elevated levels of cholesterol, particularly LDL cholesterol, in the blood.
Hypertriglyceridemia: Elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood, often associated with other lipid disorders or conditions like obesity, diabetes, or excessive alcohol consumption.
Mixed Dyslipidemia: A combination of high LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, and high triglycerides, which poses a greater risk for cardiovascular diseases.
Hypocholesterolemia (Low Cholesterol): Rare, but low cholesterol levels can also be problematic and may indicate underlying health conditions such as liver disease or malnutrition.
Causes of Lipid Problems:
- Genetics: Conditions like familial hypercholesterolemia are inherited and lead to high cholesterol from birth.
- Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars contribute to high LDL and triglyceride levels.
- Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol use can worsen lipid levels.
- Medical Conditions: Diabetes, obesity, hypothyroidism, liver or kidney disease, and certain medications can impact lipid metabolism.
Symptoms:
Lipid problems often have no symptoms in the early stages, which is why they are sometimes referred to as “silent conditions.” However, if untreated, lipid disorders can result in symptoms related to cardiovascular diseases, such as:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Heart attack or stroke (in severe cases)