
Asthma
What is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects the airways in the lungs, making them inflamed and narrowed, which leads to difficulty in breathing. It can occur in people of all ages but often begins in childhood. Asthma can vary in severity, from mild to life-threatening, and its symptoms may come and go, triggered by various factors like allergens, exercise, or stress.
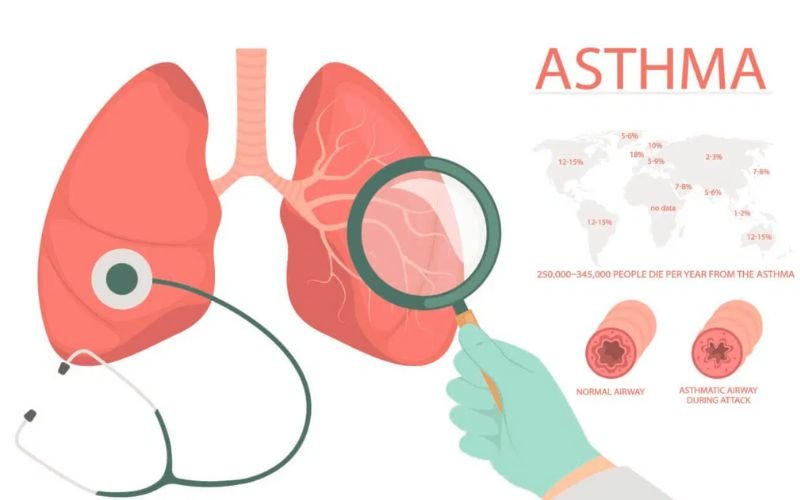
How Asthma Affects the Body:
In individuals with asthma, the airways become:
- Inflamed: The linings of the airways swell, causing them to narrow.
- Hyperreactive: The airways become overly sensitive to triggers, causing them to constrict (tighten) when exposed to irritants.
- Filled with Mucus: Excess mucus can clog the narrowed airways, further restricting airflow.
This leads to the classic symptoms of asthma, making it difficult for air to flow in and out of the lungs.
Common Symptoms of Asthma:
- Wheezing: A whistling sound while breathing, especially during exhalation.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, feeling like you can’t catch your breath.
- Chest Tightness: A feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest.
- Coughing: Persistent coughing, especially at night or early in the morning.
Asthma Triggers:
Asthma symptoms can be triggered by various environmental and internal factors, including:
- Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, mold, pet dander.
- Irritants: Smoke, strong odors, air pollution, chemical fumes.
- Exercise: Especially in cold, dry air, exercise can trigger asthma symptoms (exercise-induced asthma).
- Weather Changes: Cold air or sudden changes in temperature.
- Respiratory Infections: Colds, flu, or sinus infections.
- Stress and Emotions: Anxiety or strong emotions can sometimes trigger asthma symptoms.
Treatment of Asthma:
While asthma cannot be cured, it can be managed effectively with a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments. The goal of asthma treatment is to keep symptoms under control and prevent asthma attacks.
Medications:
- Controller Medications: These are long-term medications, often inhaled corticosteroids, that reduce inflammation in the airways and prevent symptoms. They need to be taken regularly, even when symptoms are not present.
- Quick-Relief Medications (Rescue Inhalers): These bronchodilators, like albuterol, are used to quickly relax and open the airways during an asthma attack or when symptoms flare up.
- Leukotriene Modifiers: Oral medications that help control asthma by reducing inflammation.
- Biologics: Injectable medications used for severe asthma that doesn’t respond to other treatments.
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers can significantly reduce the frequency of symptoms.
Monitoring: Using a peak flow meter to monitor lung function can help detect early signs of worsening asthma.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular exercise (with precautions for exercise-induced asthma).
- Breathing exercises to strengthen the lungs.
- A healthy diet and avoiding smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke.